Creating and Managing Oracle Tables
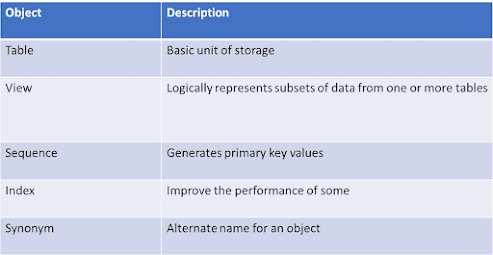
--Database Objects Lists:
Tables store our data are given as input to the oracle database. Very powerful and secured data storage devise in the world. Data is stored in the tables in a row and column format. First list the names of fields that are needed to design as required. Then create a table.
--Table
Creation
Sql> create table student
(roll number(6),
name varchar2(20),
sex char(1),CONSTRAINT STUDENT_ROLL_PK PRIMARY KEY
(ROLL));
Sql> desc tablename;
Sql>commit;
Sql> drop
table student;
Sql>commit;
--Table
Creation
Sql> CREATE
TABLE dept
(deptno
NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT PK_DEPT PRIMARY KEY,
dname
VARCHAR2(14) ,
loc
VARCHAR2(13) ) ;
--Master
Table
CREATE TABLE DEPT
(deptno
NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT PK_DEPT PRIMARY KEY,
DNAME
VARCHAR2(14) ,
LOC
VARCHAR2(13) ) ;
-- Detail Table
Sql>DROP TABLE EMP;
Sql>CREATE TABLE EMP
(EMPNO
NUMBER(4) CONSTRAINT PK_EMP PRIMARY KEY,
ENAME
VARCHAR2(10),
JOB
VARCHAR2(9),
MGR
NUMBER(4),
HIREDATE
DATE,
SAL
NUMBER(7,2),
COMM
NUMBER(7,2),
deptno
NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT FK_DEPTNO REFERENCES dept);
--Table
Remove
Sql> DROP TABLE dept;
--Create
a Table from another table (Creating Table by Subquery)
Sql> CREATE TABLE dept30
AS
SELECT empno, ename, hiredate
FROM emp
WHERE
deptno=30;
--Table
Management
Alter Tables (Add, Modify, drop) column information
Sql> ALTER TABLE dept30
ADD
(JOB VARCHAR2(9));
SQL> ALTER TABLE dept30
MODIFY
(ENAME VARCHAR2(15));
Sql>ALTER TABLE dept30
DROP
COLUMN job;
--Examining
Object Created by a User
Sql>
SELECT * FROM TAB;
--Rename
Table Name
Sql> RENAME dept TO department;
--Truncating
a Table (rows can not be rollback)
Sql> TRUNCATE TABLE department;
Comments
Post a Comment